Introduction to Vibe Coding and Atlassian Forge
What is “Vibe Coding”?
“Vibe coding” refers to using AI tools and natural language prompts to generate software code. The approach emphasizes rapid application building, often minimizing the need for extensive prior coding knowledge.
What is Atlassian Forge?
Atlassian Forge is a cloud-native development platform designed for building apps and integrations on Atlassian’s cloud infrastructure. It allows for deep customizations and extensions across products like Jira and Confluence, enabling developers to enhance functionality within these environments. You can learn more about Atlassian products like Jira on our website: Seibert Solutions Jira Licensing.
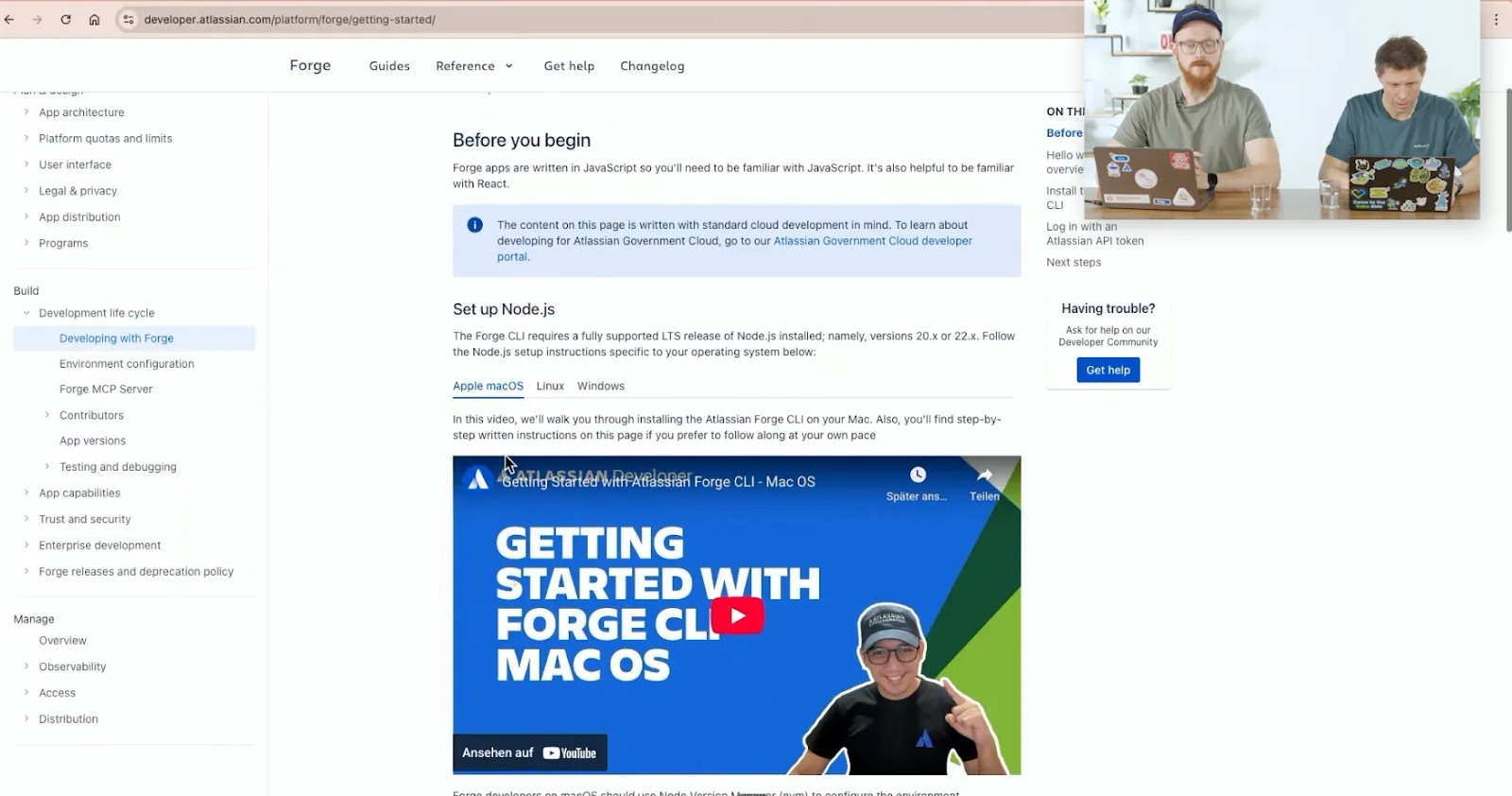
The Role of AI and Atlassian’s MCP Server
Atlassian has introduced a new Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that integrates Forge-specific knowledge directly into Integrated Development Environments (IDEs). This integration facilitates AI assistance, enabling AI tools to understand Forge modules, design tokens, and best practices, thereby streamlining the development process. For more on Forge, refer to the Atlassian Forge documentation.
Building a Jira Dashboard Gadget with AI
Setting Up the Development Environment
Developing a Forge app begins with creating a dedicated Atlassian developer site, which functions as a Jira instance for testing. Developers then configure an IDE, such as Cursor or VSCode, to integrate with Atlassian’s MCP server. The final step involves installing and logging into the Forge command-line interface (CLI) to manage app deployment.
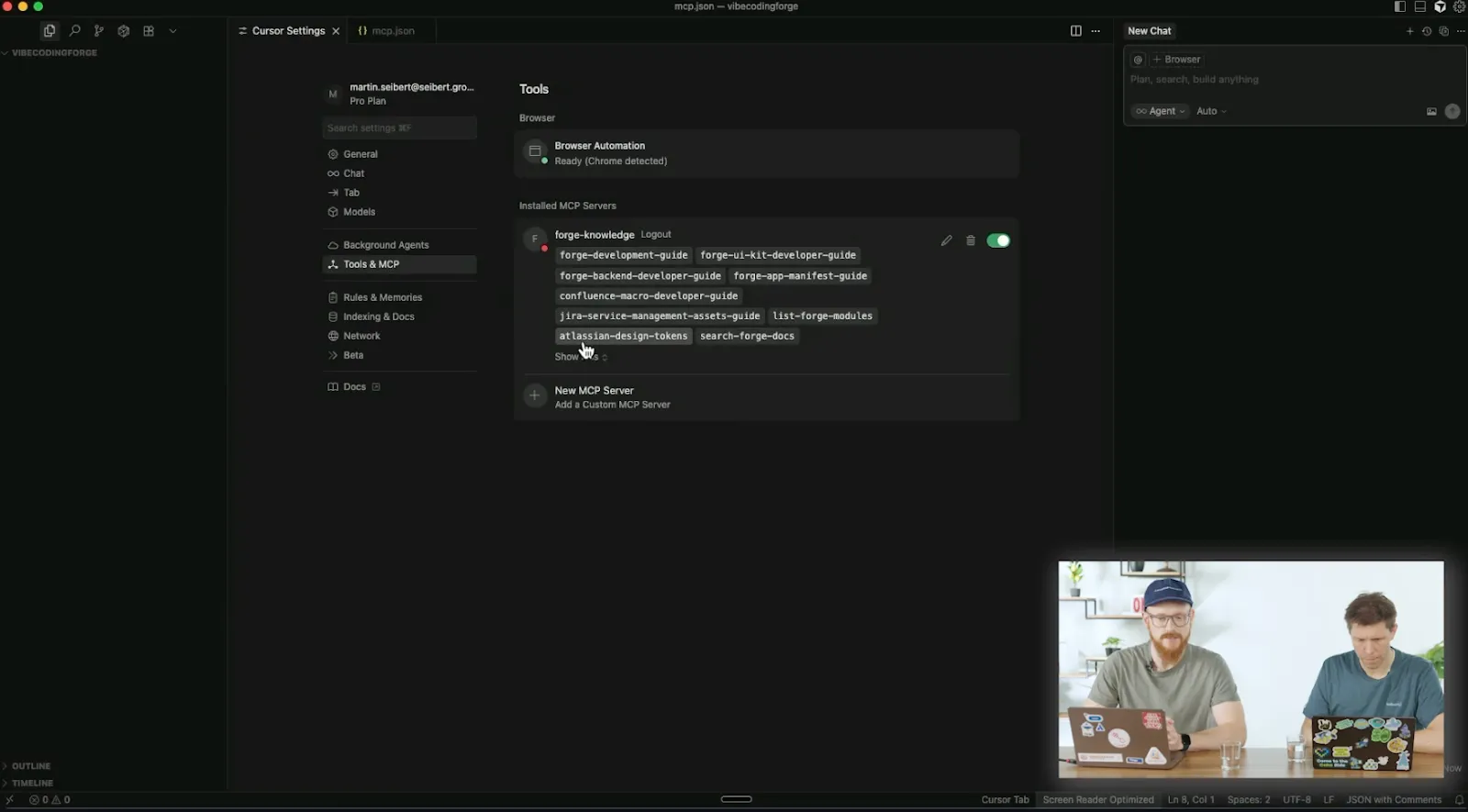
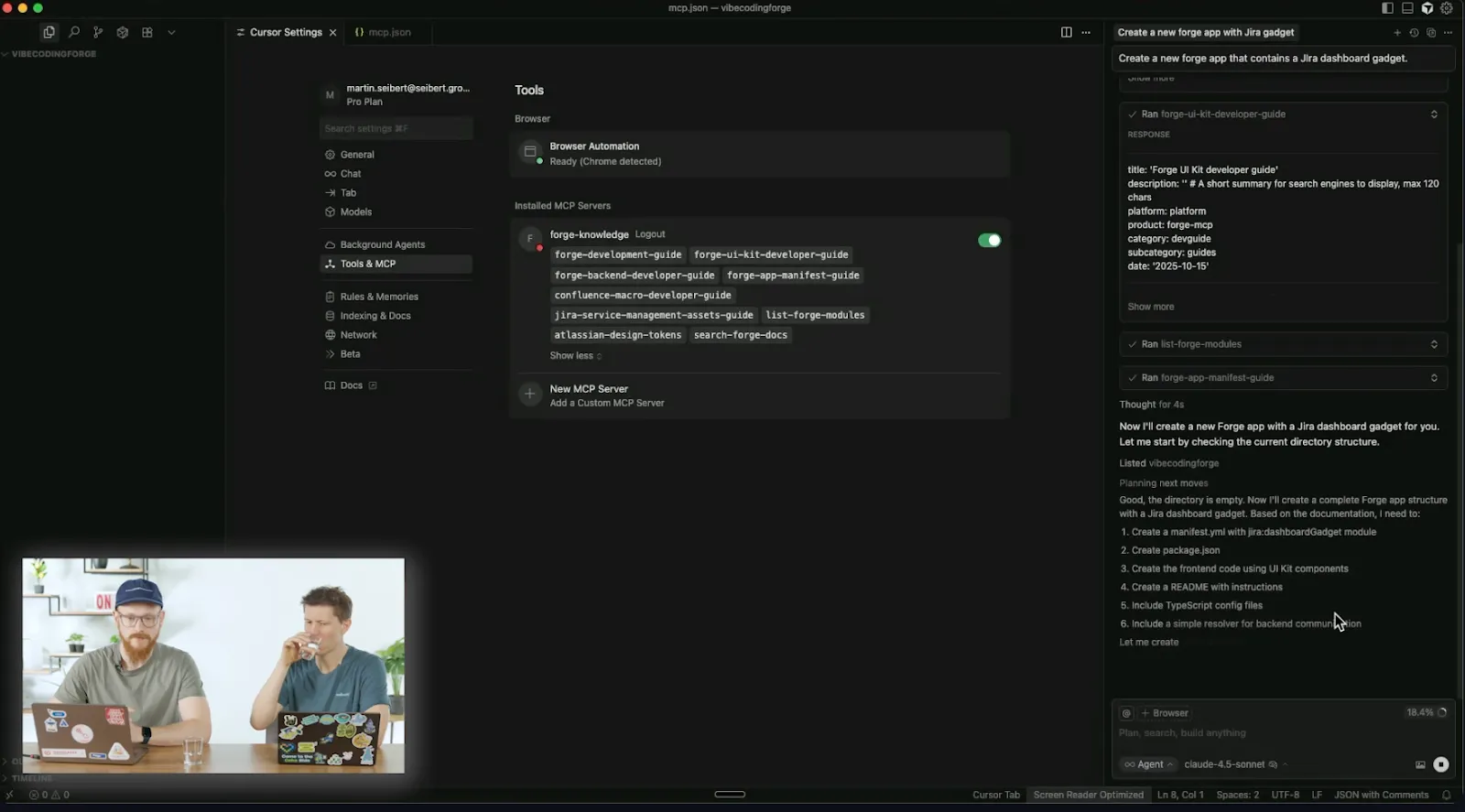
AI-Assisted App Creation
With the environment set up, AI can be prompted to create a new Forge app, such as a Jira dashboard gadget. The AI generates the initial manifest files and structures the application. This foundational code is then deployed and registered with Atlassian, establishing the app within the Forge ecosystem.
Debugging and Iteration with AI
The development process often involves troubleshooting issues like missing packages or manifest errors. AI tools can identify these problems and suggest fixes, accelerating the debugging cycle. Developers can iteratively deploy changes and test their application on the Jira instance, refining functionality until the desired outcome is achieved.
Benefits and Challenges of AI-Powered Forge Development
Advantages
-
Faster Prototyping and Time-to-Concept: AI tools enable the rapid translation of ideas into functional prototypes within Jira or Confluence, significantly reducing the time required to visualize and validate new concepts.
-
Reduced Prerequisite Knowledge for Basic Apps: AI lowers the entry barrier for individuals without extensive coding experience, allowing them to contribute to app development or create simple customizations.
-
Direct In-Platform Visualization: The ability to quickly deploy and view custom functionality directly within an Atlassian product helps stakeholders understand and provide feedback on proposed solutions.
Potential Drawbacks
-
Security Concerns: AI-generated code may contain vulnerabilities if not thoroughly reviewed by experienced developers. While Forge has baked-in security features, vigilance is necessary.
-
Need for Manual Debugging for Complex Issues: AI may struggle with highly specific or complex debugging scenarios, necessitating human intervention and expert knowledge.
-
Dependency Management and Versioning: AI might not always select the most optimal or up-to-date package versions, potentially leading to conflicts or outdated dependencies.
-
Code Quality and Maintainability: Code generated by AI may sometimes be less optimized or harder to maintain, requiring refactoring to meet production-ready standards.
Vibe Coding Recommendations for Different Roles
Junior Developers
-
Focus on Understanding the Code: Actively review and analyze AI-generated code to learn programming concepts and build foundational knowledge. This helps in understanding why the AI created specific solutions, and what’s possible with Forge.
-
Utilize Documentation and Working Examples: Combine AI assistance with official Forge documentation and working code examples to deepen understanding and cross-reference solutions.
-
Leverage AI for Explanations and Debugging Assistance: Ask AI to explain code snippets, clarify Forge modules, or assist in debugging specific error messages encountered during development.
Product Managers and Jira Administrators
-
Understand Forge Capabilities: Use AI and Atlassian documentation to explore the range of available Forge modules and extension points, informing what customizations are possible. Try asking the MCP server which modules are available.
-
Focus on Idea Generation and Specification: Clearly define use cases and desired functionality. These detailed specifications serve as effective prompts for AI, guiding it toward relevant solutions.
-
Use AI for Prototyping Ideas Quickly: Rapidly create functional prototypes to validate concepts with stakeholders and gather early feedback without significant development investment.
Senior Developers
-
Oversee Code Quality and Security: Conduct thorough code reviews, paying close attention to the Forge manifest, application scopes, and permissions to ensure security and compliance.
-
Set Up Build Pipelines and Testing: Implement automated deployment and testing pipelines to ensure the reliability and stability of Forge applications.
-
Guide Junior Developers and Facilitate Code Reviews: Mentor junior team members on coding standards, best practices, and effective debugging strategies, fostering a culture of quality.
-
Understand AI’s Limitations and Intervene for Complex Issues: Be prepared to debug, refactor, and optimize AI-generated code, especially for production-ready applications or complex scenarios where AI may fall short.
Managers
-
Establish AI Usage Policies and Boundaries: Define clear guidelines for AI-powered development within the organization, balancing the benefits of innovation with necessary governance.
-
Balance Innovation Speed with Security and Maintainability: Recognize AI’s value for rapid prototyping, but ensure that all production code undergoes human review to address security and long-term maintainability.
-
Foster Collaboration between AI-Users and Traditional Developers: Mitigate potential frustrations by clearly defining roles, handover processes, and communication channels between those using AI and experienced developers.
-
Consider AI for Prototyping, Not Necessarily Production-Ready Code: Emphasize AI as a tool for rapid ideation and proof-of-concept, understanding that experienced developers are crucial for hardening applications for production environments.
Conclusion
The Future of Atlassian Forge Development with AI
AI significantly accelerates initial development and prototyping on Atlassian Forge. It empowers developers to build customizations faster and lowers the barrier to entry for new users. However, human expertise remains crucial for complex problem-solving, ensuring security, maintaining code quality, and preparing applications for production readiness.
Partnering for Successful Customizations
Navigating the complexities of AI-powered Forge development, from initial ideation to successful deployment, can be challenging. As an Atlassian Solution Partner, Seibert Solutions offers expertise in custom Forge development. We assist organizations in leveraging AI effectively while ensuring their custom applications meet security, performance, and strategic goals. Whether you are grappling with specific problems or exploring new customization possibilities, our team is equipped to support your journey.